A look at what Snap’s S-1 reveals about their growth story and unit economics
If you follow the tech industry at all, you will have heard that consumer app darling Snap Inc. (makers of the app Snapchat) has filed to go public. The ensuing Form S-1 that has recently been made available has left tech-finance nerds like yours truly drooling over the until-recently-super-secretive numbers behind their business.

Much of the commentary in the press to date has been about how unprofitable the company is (having lost over $500M in 2016 alone). I have been unimpressed with that line of thinking — as what the bottom line is in a given year is hardly the right measure for assessing a young, high-growth company.
While full-time Wall Street analysts will pour over the figures and comparables in much greater detail than I can, I decided to take a quick peek at the numbers to gauge for myself how the business is doing as a growth investment, looking at:
- What does the growth story look like for the business?
- Do the unit economics allow for a path to profitability?
What does the growth story look like for the business?
As I’ve noted before, consumer media businesses like Snap have two options available to grow: (1) increase the number of users / amount of time spent and/or (2) better monetize users over time
A quick peek at the DAU (Daily Active Users) counts of Snap reveal that path (1) is troubled for them. Using Facebook as a comparable (and using the midpoint of Facebook’s quarter-end DAU counts to line up with Snap’s average DAU over a quarter) reveals not only that Snap’s DAU numbers aren’t growing so much, their growth outside of North America (where they should have more room to grow) isn’t doing that great either (which is especially alarming as the S-1 admits Q4 is usually seasonally high for them).
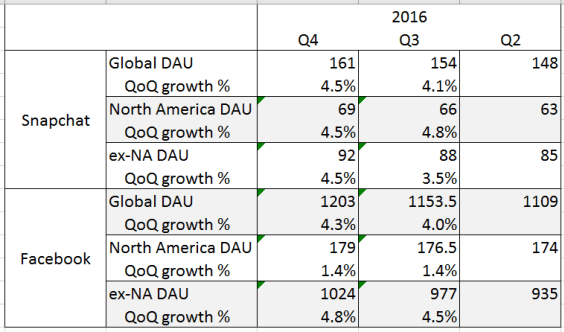
A quick look at the data also reveals why Facebook prioritizes Android development and low-bandwidth-friendly experiences — international remains an area of rapid growth which is especially astonishing considering how over 1 billion Facebook users are from outside of North America. This contrasts with Snap which, in addition to needing a huge amount of bandwidth (as a photo and video intensive platform) also (as they admitted in their S-1) de-emphasizes Android development. Couple that with Snap’s core demographic (read: old people can’t figure out how to use the app), reveals a challenge to where quick short-term user growth can come from.
As a result, Snap’s growth in the near term will have to be driven more by path (2). Here, there is a lot more good news. Snap’s quarterly revenue per user more than doubled over the last 3 quarters to $1.029/DAU. While its a long way off from Facebook’s whopping $7.323/DAU (and over $25 if you’re just looking at North American users), it suggests that there is plenty of opportunity for Snap to increase monetization, especially overseas where its currently able to only monetize about 1/10 as effectively as they are in North America (compared to Facebook which is able to do so 1/5 to 1/6 of North America depending on the quarter).
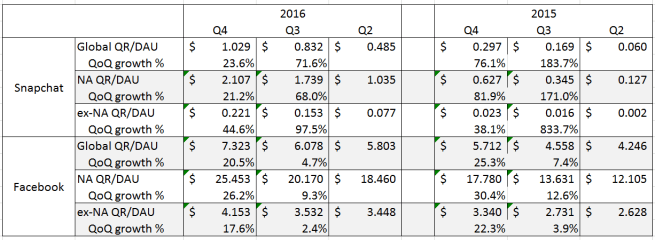
Considering Snap has just started with its advertising business and has already convinced major advertisers to build custom content that isn’t readily reusable on other platforms and Snap’s low revenue per user compared even to Facebook’s overseas numbers, I think its a relatively safe bet that there is a lot of potential for the number to go up.
Do the unit economics allow for a path to profitability?
While most folks have been (rightfully) stunned by the (staggering) amount of money Snap lost in 2016, to me the more pertinent question (considering the over $1 billion Snap still has in its coffers to weather losses) is whether or not there is a path to sustainable unit economics. Or, put more simply, can Snap grow its way out of unprofitability?
Because neither Facebook nor Snap provide regional breakdowns of their cost structure, I’ve focused on global unit economics, summarized below:
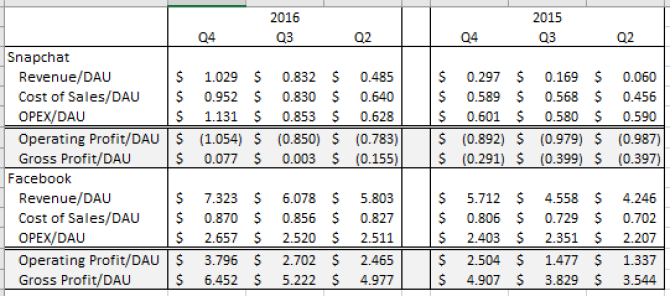
What’s astonishing here is that neither Snap nor Facebook seem to be gaining much from scale. Not only are their costs of sales per user (cost of hosting infrastructure and advertising infrastructure) increasing each quarter, but the operating expenses per user (what they spend on R&D, sales & marketing, and overhead — so not directly tied to any particular user or dollar of revenue) don’t seem to be shrinking either. In fact, Facebook’s is over twice as large as Snap’s — suggesting that its not just a simple question of Snap growing a bit further to begin to experience returns to scale here.
What makes the Facebook economic machine go, though, is despite the increase in costs per user, their revenue per user grows even faster. The result is profit per user is growing quarter to quarter! In fact, on a per user basis, Q4 2016 operating profit exceeded Q2 2015 gross profit(revenue less cost of sales, so not counting operating expenses)! No wonder Facebook’s stock price has been on a tear!
While Snap has also been growing its revenue per user faster than its cost of sales (turning a gross profit per user in Q4 2016 for the first time), the overall trendlines aren’t great, as illustrated by the fact that its operating profit per user has gotten steadily worse over the last 3 quarters. The rapid growth in Snap’s costs per user and the fact that Facebook’s costs are larger and still growing suggests that there are no simple scale-based reasons that Snap will achieve profitability on a per user basis. As a result, the only path for Snap to achieve sustainability on unit economics will be to pursue huge growth in user monetization.
Tying it Together
The case for Snap as a good investment really boils down to how quickly and to what extent one believes that the company can increase their monetization per user. While the potential is certainly there (as is being realized as the rapid growth in revenue per user numbers show), what’s less clear is whether or not the company has the technology or the talent (none of the key executives named in the S-1 have a particular background building advertising infrastructure or ecosystems that Google, Facebook, and even Twitter did to dominate the online advertising businesses) to do it quickly enough to justify the rumored $25 billion valuation they are striving for (a whopping 38x sales multiple using 2016 Q4 revenue as a run-rate [which the S-1 admits is a seasonally high quarter]).
What is striking to me, though, is that Snap would even attempt an IPO at this stage. In my mind, Snap has a very real shot at being a great digital media company of the same importance as Google and Facebook and, while I can appreciate the hunger from Wall Street to invest in a high-growth consumer tech company, not having a great deal of visibility / certainty around unit economics and having only barely begun monetization (with your first quarter where revenue exceeds cost of sales is a holiday quarter) poses challenges for a management team that will need to manage public market expectations around forecasts and capitalization.
In any event, I’ll be looking forward to digging in more when Snap reveals future figures around monetization and advertising strategy — and, to be honest, Facebook’s numbers going forward now that I have a better appreciation for their impressive economic model.
Thought this was interesting or helpful? Check out some of my other pieces on investing / finance.

Leave a Reply